

The 2018 discovery of the suspected lake set off a flurry of scientific activity, as water is closely linked with life in the solar system. While the latest findings indicate this feature is not a lake below the Martian surface, it does suggest that the same radar technique could be used to check for subsurface resources elsewhere on Mars, supporting future explorers.
The paper, published in Geophysical Research Letters on Nov. 17, was led by two of MRO’s Shallow Radar (SHARAD) instrument scientists, Gareth Morgan and Than Putzig, who are based at the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and Lakewood, Colorado, respectively.

Morgan, Putzig, and fellow SHARAD team members had made multiple unsuccessful attempts to observe the area suspected of hosting a buried lake. Then the scientists partnered with the spacecraft’s operations team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which leads the mission, to develop the very large roll capability.
Because the radar’s antenna is at the back of MRO, the orbiter’s body obstructs its view and weakens the instrument’s sensitivity. After considerable work, engineers at JPL and Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, which built the spacecraft and supports its operations, developed commands for a 120-degree roll — a technique that requires careful planning to keep the spacecraft safe — to direct more of SHARAD’s signal at the surface.
A bright signal #
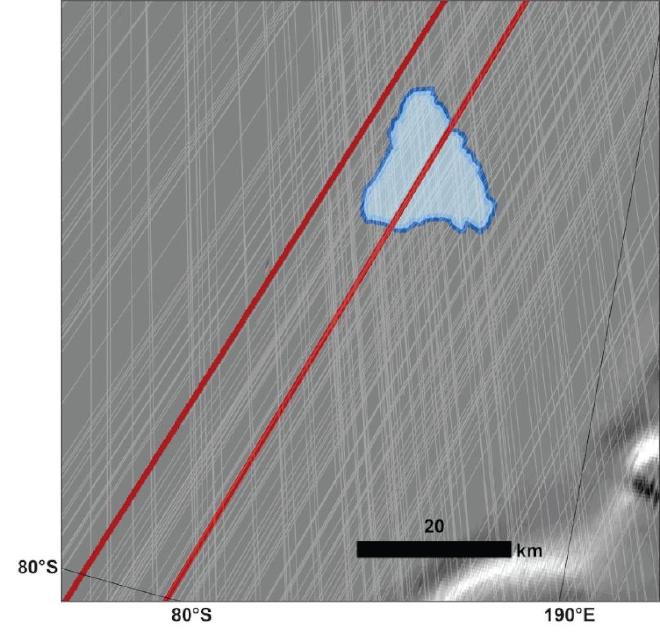
On May 26, SHARAD performed a very large roll to finally pick up the signal in the target area, which spans about 12.5 miles (20 kilometers) and is buried under a slab of water ice almost 1 mile (1,500 meters) thick.
When a radar signal bounces off underground layers, the strength of its reflection depends on what the subsurface is made of. Most materials let the signal slip through or absorb it, making the return faint. Liquid water is special in that it produces a very reflective surface, sending back a very strong signal (imagine pointing a flashlight at a mirror).
“We’ve been observing this area with SHARAD for almost 20 years without seeing anything from those depths,” said Putzig. But once MRO achieved a very large roll over the precise area, the team was able to look much deeper. And rather than the bright signal MARSIS received, SHARAD detected a faint one. A different very-large-roll observation of an adjacent area didn’t detect a signal at all, suggesting something unique is causing a quirky radar signal at the exact spot MARSIS saw a signal.
“The lake hypothesis generated lots of creative work, which is exactly what exciting scientific discoveries are supposed to do,” said Morgan. “And while this new data won’t settle the debate, it makes it very hard to support the idea of a liquid water lake.”
Alternative explanations #
Mars’ south pole has an ice cap sitting atop heavily cratered terrain, and most radar images of the area below the ice show lots of peaks and valleys. Morgan and Putzig said it’s possible that the bright signal MARSIS detected here may just be a rare smooth area — an ancient lava flow, for example.
“If it’s ice, that means there’s lots of water resources near the Martian equator, where you’d want to send humans,” said Putzig. “Because the equator is exposed to more sunlight, it’s warmer and ideal for astronauts to live and work.”
Citation #
- The study High Frequency Radar Perspective of Putative Subglacial Liquid Water on Mars was published in Geophysical Research Letters. Authors: Gareth A. Morgan, Matthew R. Perry, Bruce A. Campbell, Nathaniel E. Putzig, Jennifer L. Whitten & Fabrizio Bernardini
Funding #
NASA MRO Project to the U.S. SHARAD Science Team through the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Grant Numbers: 1593870, 1640185
- The article NASA Orbiter Shines New Light on Long-Running Martian Mystery was published in JPL’s news website with Andrew Good, from JPL and Karen Fox / Molly Wasser from NASA Headquarters involved in what you’ve just read. Many thanks from Notaspampeanas for all that were involved in the issue!!!.
Contact [Notaspampeanas](mailto: notaspampeanas@gmail.com)

