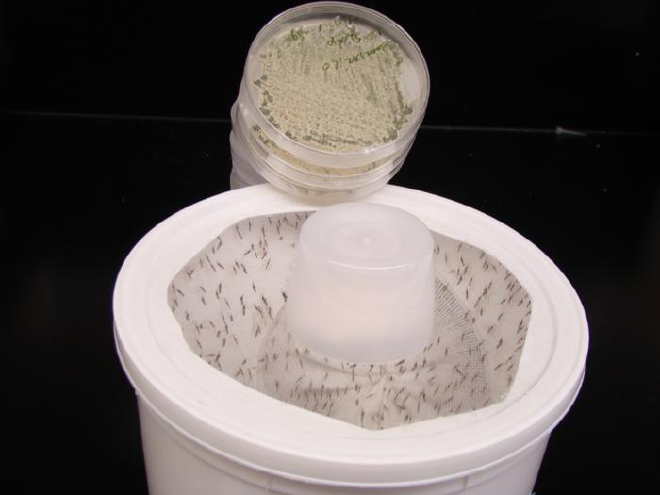

Taking advantage of the mosquito’s natural attraction to flowers, an international team of researchers engineered a new strain of Metarhizium fungus that imitates a flower’s sweet scent and lures the bloodsucking bugs to their deaths.
“Mosquitoes need flowers because they provide nectar, a crucial source of food for them, and they are drawn to flowers through their scents,” explained paper co-author Raymond St. Leger, a Distinguished University Professor of Entomology at the University of Maryland. “After observing that some types of fungi could trick mosquitoes into thinking they were flowers, we realized we could turbo-charge the attraction by engineering fungi to produce more longifolene, a sweet-smelling compound that’s already very common in nature. Before this study, longifolene wasn’t known to attract mosquitoes. We’re letting nature give us a hint to tell us what works against mosquitoes.”
St. Leger noted that the floral-scented fungus is an easy-to-use control method against mosquitoes, requiring little to no training or specialized knowledge. As soon as the fungus spores are placed in a container, either indoors or outdoors, longifolene is instantly and gradually released, maintaining effectiveness for months. Once mosquitoes encounter the fungus, they become infected and die within days. In lab tests, the fungus killed 90 to 100% of mosquitoes—even when placed in a large room with competing scents from humans and real flowers. Although the fragrant fungus is deadly to mosquitoes, it is harmless to humans.
In addition, unlike chemical alternatives that mosquitoes have gradually become resistant to, this biological approach may be nearly impossible for mosquitoes to outsmart or avoid.
“If mosquitoes evolve to avoid longifolene, that could mean they’ll stop responding to flowers,” St. Leger explained. “But they need flowers as a food source to survive, so it would be very interesting to see how they could possibly avoid the fungus yet still be attracted to the flowers they need. It’ll be very difficult for them to overcome that hurdle, and we have the option of engineering the fungus to produce additional floral odors if they evolve to specifically avoid longifolene.”
What also makes this new fungal technology particularly promising is how practical and affordable it is to produce. Other forms of Metarhizium are already commonly cultivated around the world on cheap materials like chicken droppings, rice husks and wheat scraps that are readily available after harvest. The affordability and simplicity of the fungus could be key to reducing mosquito disease-related deaths in many parts of the world, especially in poorer countries in the global south.
“Mosquitoes love many of the ways we are changing our world,” St. Leger said. “Right now, we’re hoping to use these approaches in Africa, Asia and South America. But one day, we may need them for ourselves.”
St. Leger and his collaborators are currently working on larger-scale outdoor trials of their mosquito control method to submit for regulatory approval.
Citation #
- The study Engineered Metarhizium fungi produce longifolene to attract and kill mosquitoes,” was published in Nature Microbiology was published in Nature Microbiology. Authors: Dan Tang, Jiani Chen, Yubo Zhang, Xingyuan Tang, Xinmiao Wang, Chaonan Yu, Xianxian Cheng, Junwei Zhang, Wenqi Shi, Qing Zhen, Shuxing Liu, Yizhou Huang, Jiali Ning, Guoding Zhu, Meichun Zhang, Juping Hu, Etienne Bilgo, Abdoulaye Diabate, Sheng-Hua Ying, Jun Cao, Raymond J. St. Leger, Jianhua Huang & Weiguo Fang
Acknowledgements #
Researchers thanked M. Jiang and X. Wang from the Institute of Insect Science at Zhejiang University for providing experimental insects. We thank Y. Chen and Y. Xu at Zhejiang University for help with SPME–GC–MS analysis, D. Lou at Zhejiang University for help with video recording and X. Deng at Nanjing Medical University for help with statistical analysis. We recognize the indispensable efforts of undergraduate students at Zhejiang University involved in this study (H. Jiang, Y. Yang and J. Liu). This work was funded by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China to W.F. (82261128002, 32172470) and to J. Huang (32325044), Gates Foundation (INV-070892) and ‘Pioneer’ and ‘Leading Goose’ R&D Program of Zhejiang (2023C02025) to W.F., and National Key R&D Program of China (number 2023YFA1801004) to J. Cao.
Ethics declarations #
Competing interests #
D.T. and W.F. filed a patent application (Chinese Patent application no. 202210069879.X, published April 27, 2022). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Contact [Notaspampeanas](mailto: notaspampeanas@gmail.com)

