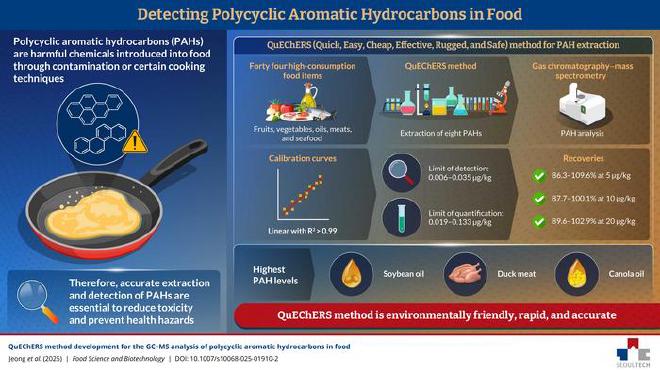
Today, people are increasingly prioritizing their health and well-being, with daily exercises and calorie-tracking apps becoming the new norm. People are therefore interested in incorporating highly nutritious food items such as fruits and vegetables into their diet plans. However, these foods—owing to contamination as well as due to certain cooking methods such as heating, smoking, grilling, roasting, and frying—may contain polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) (hydrophobic organic compounds comprising multiple fused aromatic rings) and their derivatives. PAHs comprise some carcinogenic compounds, posing significant risks to human health.
In a new study, a team of researchers from the Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Seoul National University of Science and Technology, led by Professor Joon-Goo Lee, utilized the QuEChERS method to determine eight PAHs Benzo[a]anthracene, Chrysene, Benzo[b]fluoranthene, Benzo[k]fluoranthene, Benzo[a]pyrene, Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene, Dibenz[a,h]anthracene, and Benzo[g,h,i]perylene in food. Their findings were made available online on 5 June 2025 and were published in Volume 34, Issue 12 of the journal Food Science and Biotechnology in August 2025.
The researchers extracted PAHs using acetonitrile. This was followed by purification via different methods involving various combinations of sorbents. The researchers validated the QuEChERS extraction method through a number of food matrices, finding that the calibration curves for the eight PAHs demonstrated remarkable linearity, with the R2 value exceeding 0.99.
Professor Lee noted that “this method not only simplifies the analytical process but also demonstrates high efficiency in detection compared to conventional methods. It can be applied to a wide range of food matrices.”
Overall, this study showcases that the developed PAH analysis method based on the QuEChERS approach is environmentally friendly, rapid, and accurate.
“Our research can improve public health by providing safe food. It also reduces the use and emission of hazardous chemicals in laboratory testing,” concluded Professor Lee.
Citation #
- The paper QuEChERS method development for the GC–MS analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food - Food Science and Biotechnology was published in Food Science and Biotechnology. Authors: Jihun Jeong, Minju Koo & Joon-Goo Lee.
Contact [Notaspampeanas](mailto: notaspampeanas@gmail.com)

