
Acupuncture treatment on the DU channel1 has shown therapeutic effects for Alzheimer’s disease(AD), but the underlying mechanisms are not yet clear. The purpose of the study, spotted here, was to comprehensively observe the protective effects of acupuncture on different brain regions in AD model mice, providing laboratory evidence for clinical acupuncture intervention in AD.
Methods #
Eleven senescence-resistant strain 1 male mice were used as the normal control group. The senescence-accelerated prone strain 8 (SAMP8) male mice were used as AD model mice. Thirty-three SAMP8 mice were randomly divided into three groups: AD model group (group M), drug treatment group, and acupuncture treatment group (group A). The effect of acupuncture on learning and memory capabilities of SAMP8 mice was assessed by the Morris water maze test. Nissl staining was employed to provide a general view of the brain structure in AD model mice. Additionally, Western blot analysis was used to quantify Caspase-3 and tau protein levels.
Results #
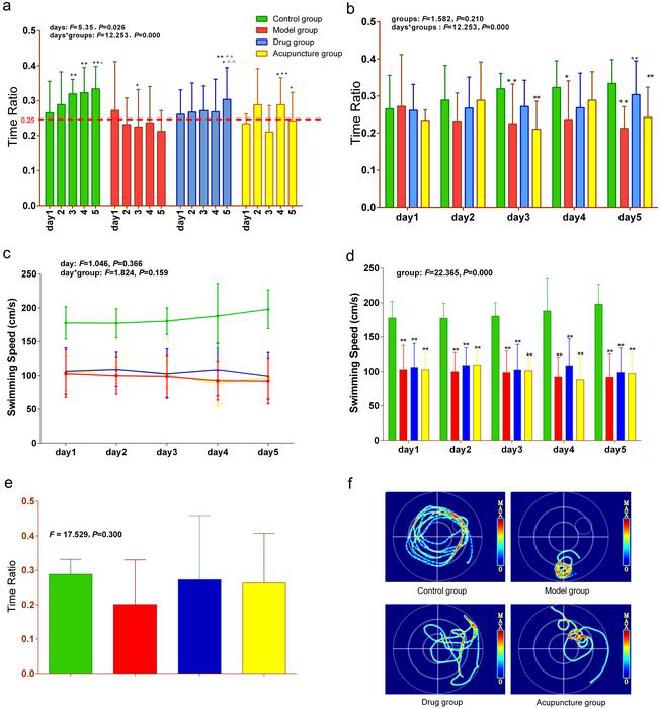
In the spatial navigation test, the ratio of time mice spent in the goal quadrant in group M remained low, even lower than 25%. The ratio of time spent in the goal quadrant by mice in the acupuncture group on day 4 was higher than that on day 1 (P < 0.01). There was a trend indicating that the time ratio of mice in the acupuncture group during the probe trial was higher than in group M, though there was no statistically significant difference. Most traces of mice in group A were in the goal platform quadrant and across the platform in different, yet effective, ways. Compared to group M, most of the cells in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, and temporal cortex of mice in group A were round with clear stratification, regular arrangement, and increased Nissl bodies. The content of Caspase-3 in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of mice in the acupuncture group was lower than in group M (P < 0.01, P < 0.05). The content of tau in the hippocampus and temporal cortex of mice in group A was lower than in group M (P < 0.05; P < 0.01).
Conclusions #
Acupuncture at the DU channel can improve learning and memory abilities, as well as depression-like behavior, to a certain degree by reducing apoptosis in the frontal cortex and hippocampus and by decreasing the deposition of tau in the hippocampus and temporal cortex of AD model rats. Further research should focus on the multiple effects and mechanisms of acupuncture for AD, as well as its impact on accompanying symptoms such as depression-like behavior.
- The paper Acupuncture Protects Brain Regions in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model by Inhibiting Apoptosis and Reducing Tau Protein was published in Future Integrative Medicine. Authors: Huiling Tian, Yujie Li, Shun Wang, Zidong Wang, Jiayi Yang, Hao Liu, Jingyu Ren, Jiheng Zuo, Yushan Gao, Ruosang Du, Zhigang Li, Xin Wang & Jing Jiang
-
The Du (Governing) Channel, also known as the Sea of Yang, is a significant meridian in acupuncture. It runs along the midline of the back and head, starting from the perineum and ascending through the spine to the upper lip. Some key points along the Du Channel: GV-2 (Yaoshu): Located at the lower back, this point is known as the Low Back Transporter. It can be used to treat lower back pain and other related issues. GV-20 (Baihui): Situated at the top of the head, this point is often used to treat vertigo, ear and nasal disorders, and various mental disorders. GV-14 (Dazhui): Found between the 7th cervical vertebra and the 1st thoracic vertebra, this point is commonly used to treat fever, stiffness in the neck and back, and respiratory issues. GV-16 (Fengfu): Located at the midpoint of the posterior neck, this point can be used to treat headaches, neck pain, and mental disorders. GV-24 (Shangxing): Situated at the midpoint of the forehead, this point is used to treat headaches, dizziness, and eye disorders. Sources: Atlas of Acupuncture Points; Acupunture Channels and Points; Acupuncture is my life; Science; Won Institute; English Wikipedia ↩︎

